Revision 2f7888b5e6a3f44c7b9a9b3bc1fdf8667ce16d70 (click the page title to view the current version)
Lecture on Rational Agents
Overview -> Rational Agents -> lecture
Briefing
- What is AI?
- Act or think? Humanly or rationally?
The Agent
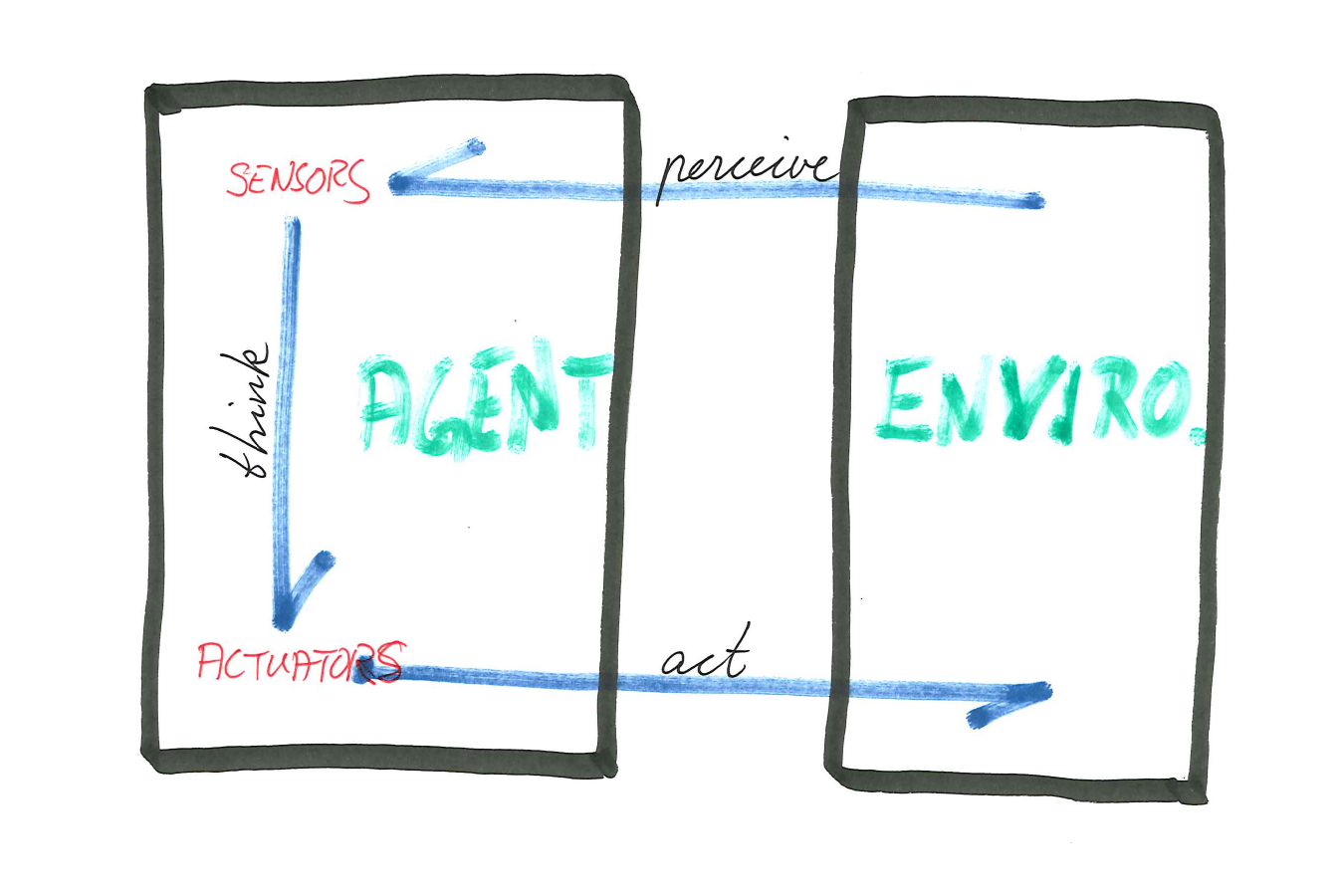
- Agent: perceive and act
- vs machine learning
- A rational agent is one that chooses the right action.
- what is right?
- Hume on is-ought
- Predefined goal
- Aristotle’s algorithm implemented by Newell & Simon (GPL)
- means-ends analysis
- we deliberate on means, not on ends
PEAS
- PEAS - Performace Measure, Environment, Actuators, Sensors
Task Environment
- Properties of the Environment
- Fully or partially observable
- can you sense all relevant aspects?
- Single or multi-agent
- what is an agent?
- do actions influence other agent?
- game theory - can you predict other agent’s actions?
- Deterministic or not
- Episodic or sequential
- memory
- Static or dynamic
- can it change while you think?
- round-based games are static
- Discrete or continuous
- discrete state space
- discrete time
- Known or unknown
- do you have a complete model of the world?
- a known world may have unknown or stochastic states
- Fully or partially observable
Paradigms or Program Type
- simple reflex agent
- model-based agents
- goal-based agents
- utility-based agents
- learning agents
- Problem Generator
