Revision 65cffde498940e8535c61d970fff80685ec95c27 (click the page title to view the current version)
Image Formation
Vision is the inverse problem of image formation
- perspective
Briefing
Image Representation
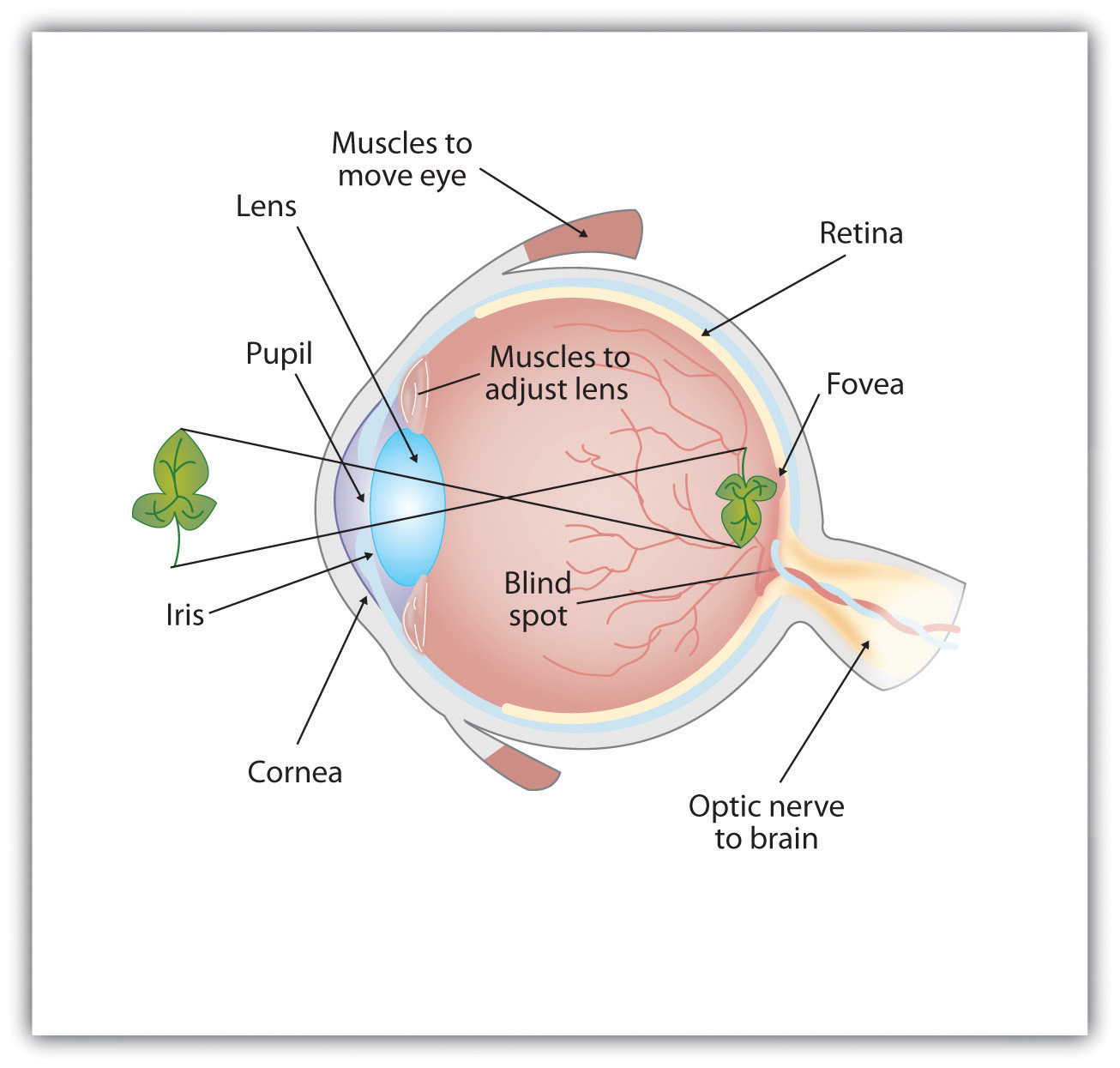
- Eye model
- Viewpoints
- 2D matrix
- light intensity values
- `image’
- Sampling of the image
- finite resolution
Thin Lens Model
The Focus Point
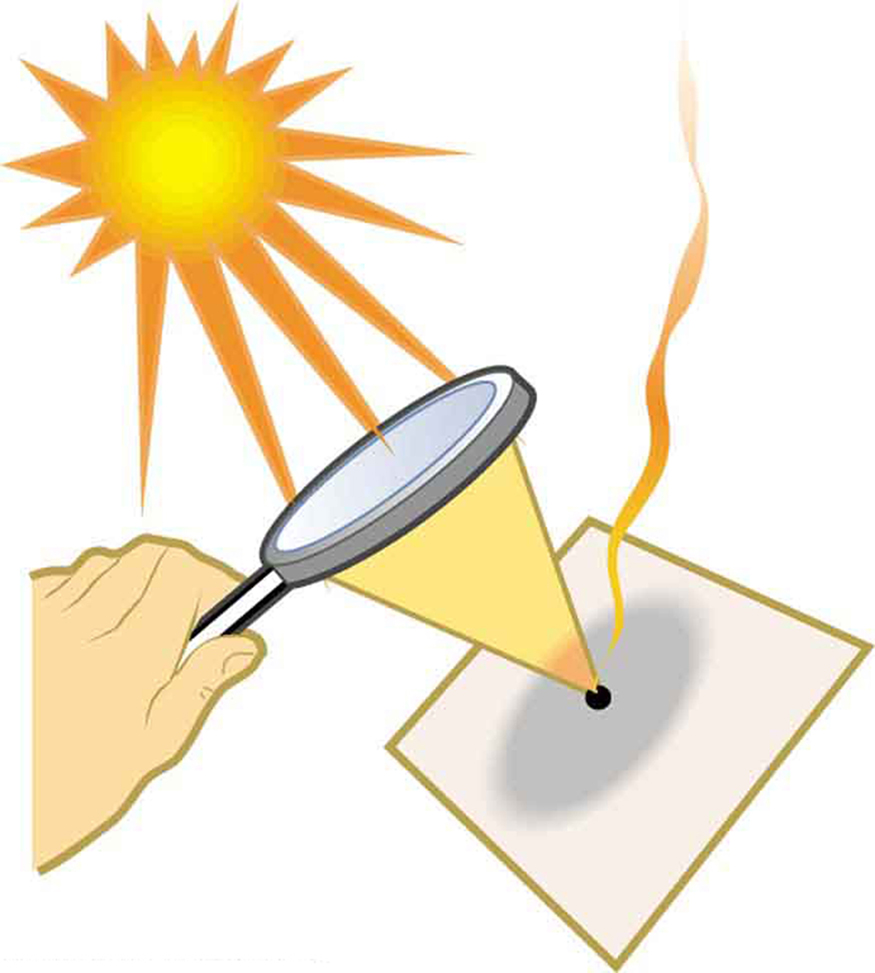

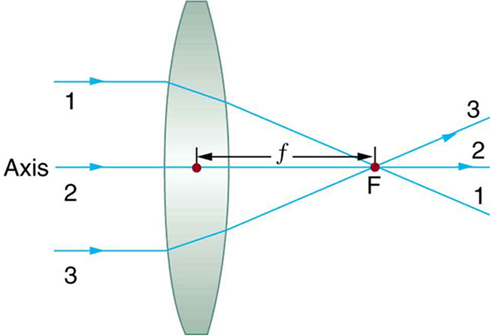
- A convex lens collect, or focus, parallel rays into a single focus point.
- This works as a burning glass.
- The sun is so far away that the sun rays are parallel for all practical purposes.
- Definitions
- Optical Axis is the line perpendicular on the lens, through its centre.
- The Focus is a point on the Optical Axis. Rays which enter the lense parallel to the optical axis are deflected so that they intersect at the Focus.
- Focal Length is the distance between the lens and the Focus. (We ignore the thickness of the lens.)
- The Focal Plane is a plane through the Focus, perpendicular on the Optical Axis.
The Image Plane
- The image plane
- non-parallel rays
- The thin lens equation
- Points further away
- The aperture
The pinhole model
- Reference frame
- Co-ordinates
Geometry of Image Formation
Exercises
Debrief
Credits
Introduction to Psychology by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
College Physics. Authored by: OpenStax College. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Located at License
